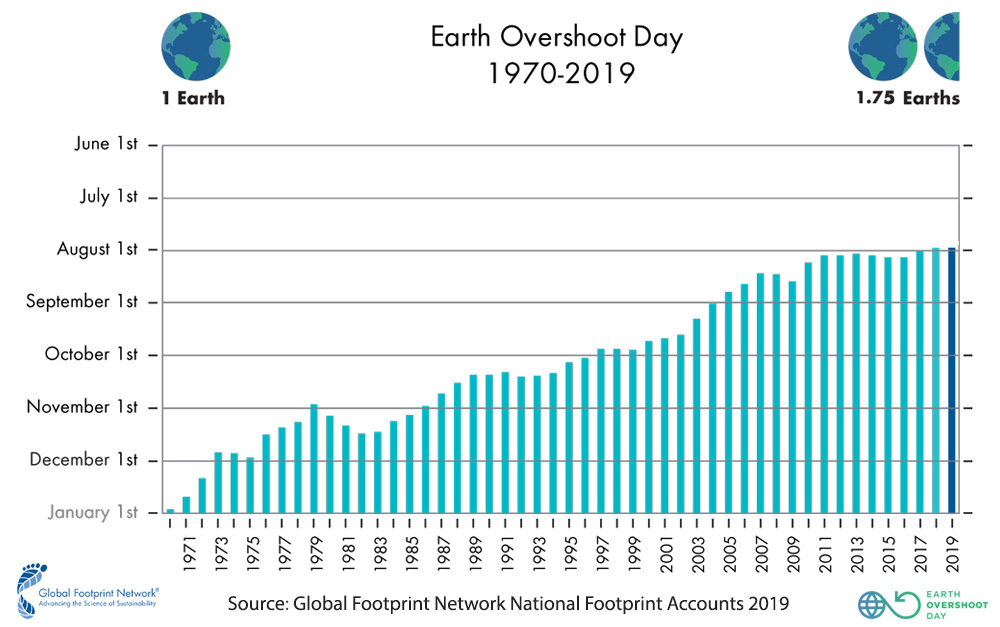
World marks earliest ‘Earth Overshoot Day’
The equivalent of 1.75 planets would be required to produce enough to meet humanity’s needs at current consumption rates. Mankind will have used up its allowance of natural resources such as water, soil and clean air for all of 2019 by today.
Earth Overshoot Day marks the date when humanity’s demand for ecological resources and services in a given year exceeds what Earth can regenerate in that year. We maintain this deficit by liquidating stocks of ecological resources and accumulating waste, primarily carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Earth Overshoot Day is hosted and calculated by Global Footprint Network, an international research organization that provides decision-makers with a menu of tools to help the human economy operate within Earth’s ecological limits.

Starting Monday, humanity will consume more resources through the end of 2019 than the planet can sustainably regenerate for the year, according to the Global Footprint Network (GFN), which has been calculating Earth Overshoot Day since 1986. In other words, mankind will have used up its allowance of natural resources such as water, soil and clean air for all of 2019 by today.
The GFN totals usage of food, timber, fibers, carbon sequestration and more. Currently, carbon emissions from burning fossil fuel constitute 60% of humanity’s ecological footprint.
On the supply side, a city, state, or nation’s biocapacity represents its biologically productive land and sea area, including forest lands, grazing lands, cropland, fishing grounds, and built-up land.
On the demand side, the Ecological Footprintmeasures a population’s demand for plant-based food and fiber products, livestock and fish products, timber and other forest products, space for urban infrastructure, and forest to absorb its carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels.
Both measures are expressed in global hectares—globally comparable, standardized hectares with world average productivity. A hectare is equivalent to 10,000 square meters or 2.47 acres
Each city, state or nation’s Ecological Footprint can be compared to its biocapacity. If a population’s demand for ecological assets exceeds the supply, that region runs an ecological deficit. A region in ecological deficit meets demand by importing, liquidating its own ecological assets (such as overfishing), and/or emitting carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
At the global level, ecological deficit and overshoot are the same, since there is no net import of resources to the planet.
History
The concept of Earth Overshoot Day was first conceived by Andrew Simms of the UK think tank New Economics Foundation, which partnered with Global Footprint Network in 2006 to launch the first global Earth Overshoot Day campaign. At that time, Earth Overshoot Day fell in October. WWF, the world’s largest conservation organization, has participated in Earth Overshoot Day since 2007.
By the GFN’s calculations, some countries reach their own overshoot days much more quickly than others. Qatar and Luxembourg overshoot the mark less than 50 days into the year, while the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, the US, Canada, Denmark and Australia burn through their allotted resources before the end of March. Israel and Germany hit their overshoot point on May 3, and only Cuba, Nicaragua, Iraq, Ecuador and Indonesia don’t reach the mark until December.
Past Earth Overshoot Days
Information courtesy: overshootday.org




