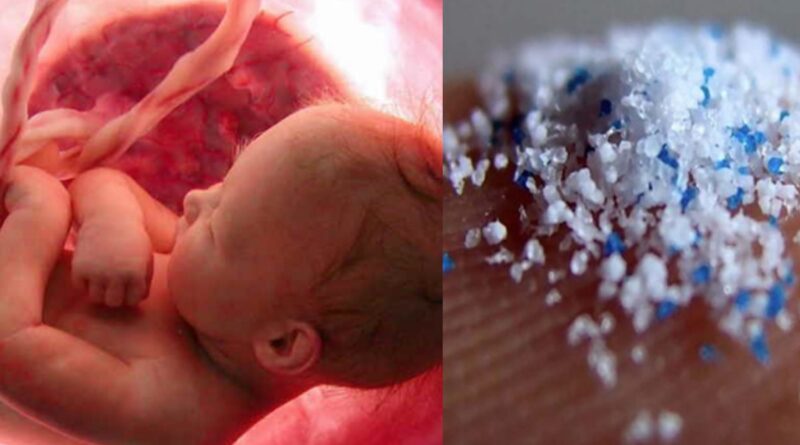
Microplastics revealed in the placentas of unborn babies
Microplastic particles have been revealed in the placentas of unborn babies for the first time, which the researchers said was “a matter of great concern”.
The health impact of microplastics in the body is as yet unknown. But the scientists said they could carry chemicals that could cause long-term damage or upset the foetus’s developing immune system. The particles are likely to have been consumed or breathed in by the mothers.
Placentas from four healthy women had microplastic particles in it. Both the foetal and maternal sides of the placenta had traces of microplastics. Even the membrane inside which the foetus grows had microplastics particles in them. However, all four pregnancies were normal and all mothers and newborn babies were healthy.
Throughout the study process, the researchers ensured a stringent plastic-free environment protocol in order to prevent any contamination of the placentas during delivery of the babies. The doctors and the midwives or nurse wore cotton gloves during the delivery of the babies.

A dozen plastic particles were found. Only about 4% of each placenta was analysed, however, suggesting the total number of microplastics was much higher. All the particles analysed were plastics that had been dyed blue, red, orange or pink and may have originally come from packaging, paints or cosmetics and personal care products.
The microplastics were mostly 10 microns in size (0.01mm), meaning they are small enough to be carried in the bloodstream. The particles may have entered the babies’ bodies, but the researchers were unable to assess this.
In the study, published in the journal Environment International, the researchers concluded: “Due to the crucial role of placenta in supporting the foetus’s development and in acting as an interface with the external environment, the presence of potentially harmful plastic particles is a matter of great concern. Further studies need to be performed to assess if the presence of microplastics may trigger immune responses or may lead to the release of toxic contaminants, resulting in harm.”
The potential effects of microplastics on foetuses include reduced foetal growth, they said. The particles were not found in placentas from two other women in the study, which may be the result of different physiology, diet or lifestyle, the scientists said.
Microplastics pollution has reached every part of the planet, from the summit of Mount Everest to the deepest oceans. People are already known to consume the tiny particles via food and water, and to breathe them in.
Their effect in the body is unknown but scientists say there is an urgent need to assess the issue, particularly for infants. In October, scientists revealed that babies fed formula milk in plastic bottles are swallowing millions of particles a day. In 2019, researchers reported the discovery of air pollution particles on the foetal side of placentas, indicating that unborn babies are also exposed to the dirty air produced by motor traffic and fossil fuel burning.
The Italian researchers used a plastic-free protocol to deliver the babies in order to prevent any contamination of the placentas. Obstetricians and midwives used cotton gloves to assist the women in labour and only cotton towels were used in the delivery room.
A separate recent study showed that nanoparticles of plastic inhaled by pregnant laboratory rats were detected in the liver, lungs, heart, kidney, and brain of their foetuses.